Digestive
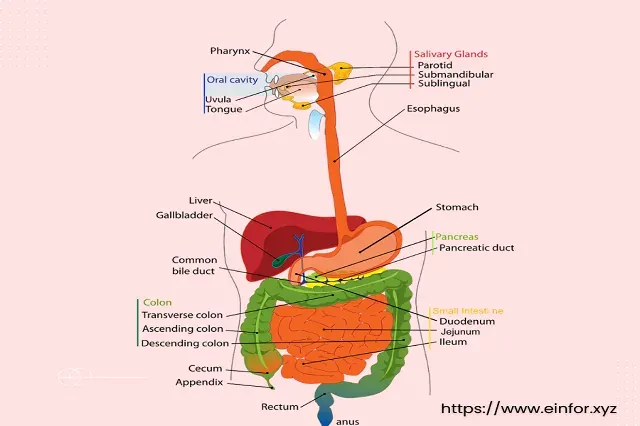
The digestive system consists of a group of organs, most of which are located within the gastrointestinal tract or as it is also known as the gastrointestinal tract and abbreviated GI tract, which is a group of hollow organs connected to each other, which form a twisted tube that extends from mouth to anus, in addition to another group of organs represented by the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas, and it is worth noting that the length of the digestive system varies from person to person and may reach a length of eight meters in total, as the length of the esophagus varies between 23-25.4 centimeters, the size of the small intestine reaches about seven meters and the large intestine or colon to about one and a half meters.
Organs of the digestive system
- The primary function of the digestive system is to extract the necessary energy for the body from food and to convert unconsumed food residues into waste products to be disposed of outside the gut and body, so the organs of the digestive system have a unique shape and structure that helps them to accomplish this task accurately, and the following is a statement of the organs of the digestive system and the function of each of them:
- Mouth: It is the first part of the digestive tract and the digestion process begins when food enters it, as it is chewed to cut food into small parts to facilitate digestion, in addition to the secretion of saliva, which in turn helps to divide food into parts that are easy to absorb and use in the body.
- Esophageal: Food moves from the mouth to the esophagus begins in the throat area and extends next to the trachea to the stomach, and food in the esophagus travels through a group of muscle contractions known as peristalsis or worm movement and is the main part of the food pathway.
- Stomach: After the food moves to the stomach, mechanical and chemical digestion begins by mixing food with various digestive enzymes, chlorine acid compounds, or hydrochloric acid, and the stomach has the ability to contain approximately 4 liters of food.
- Small intestine: Food moves from the stomach to the small intestine, which is the most important organ of the digestive system, where 90% of the different parts of food are digested, which is a thin and long tube estimated to be 6.7 meters long and consists of three main parts represented by duodenum or duodenum, fasting, and ileum, and the transport of food in the small intestine depends on worm movement as well, and most of the digestion and breakdown of food in the intestine occurs in the duodenal area, it is the area where enzymes are secreted The digestive pancreas and bile juice, while most of the nutrients are absorbed from the fasting and ileal areas, it is worth noting that food moves to the intestine from the stomach with a semi-solid texture, and as it exits from the small intestine to the large intestine it has an almost liquid texture.
- Large intestine: The large intestine is divided into the cecum that connects to the appendix, ascending colon, transverse colon, and descending colon, and in the large intestine part of the remaining nutrients and water is absorbed from food to turn from liquid to solid state again, with the formation of feces which in turn mainly contains food residues and bacteria, and then the feces are stored in the area known as the sigmoid colon before moving to the rectum and anus to be eliminated outside the body, and it is worth mentioning The beneficial bacteria present in the large intestine have an important role in digestion as well, helping to process some parts of food and waste, producing some vitamins, as well as protecting against some types of harmful bacteria.
- Rect: The rectum is about 20 centimeters long and is located at the end of the colon, connecting the large intestine and anus, and is responsible for sending nerve signals to the brain to alert about the arrival of feces or gases to the rectum, so that the brain, in turn, sends nerve commands that allow waste and gases to pass, or store them in the rectum until another time.
- Anus: It is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract, from which the stool is thrown out of the body, and the anus consists of the muscles of the pelvic floor, the internal sphincter muscle, and the external sphincter, which work in coordination with each other to prevent the exit of feces unless the process of defecation is voluntarily controlled, and the upper part of the lining of the anus contains sensitive receptors that reveal the nature of the waste products present at the sphincter muscle whether they are of a gaseous, fluid, or solid nature, and here it is worth noting that The stool naturally contains solid waste from food, while liquid waste is excreted with urine.
- Liver: The liver purifies the blood coming from the small intestine before it moves to other parts of the body, and it also removes toxins and harmful chemical elements, in addition to the production of many chemical elements important to the body, and the production of bile that is stored in the gallbladder before being excreted in the intestine.
- Gallbladder: The gallbladder stores the bile that is produced in the liver and increases its concentration before it is excreted to the duodenal region of the intestine, which in turn facilitates the digestion and absorption of fat.
- Pancreas: It produces many important enzymes in the pancreas that help digest fats, proteins, carbohydrates, or sugars, as these enzymes are secreted in the duodenal region of the small intestine, and the hormone insulin is produced from the pancreas to the bloodstream, which is the main hormone responsible for the metabolism of sugar and its utilization in the body.
Digestive function
The function of the digestive system is to convert food and liquids into their basic elements, such as fats, proteins, vitamins, and carbohydrates to be utilized, as these elements cannot be absorbed from the digestive system through the blood before converting them from their complex large forms into small and simple forms, and after absorbing these elements are used in the body to repair cells, growth, and energy production, and the duration of digestion is estimated between 2-5 days from the entry of food through the mouth until its disposal through the anus in normal cases, as it needs an operation Food is digested in the stomach and intestines for 6-8 hours, while food needs about 36 hours to pass through the colon, and it is worth noting that the duration of digestion varies between individuals, and between men and women.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
There are many diseases and health problems that may affect the digestive system, and here are some of them:
- Diverticulitis: A group of hollow bulges may form in the intestine over time known as diverticulitis or diverticulitis, and most often this diverticulitis does not pose any health problems in the person, and in some cases, this diverticulum may be exposed to infection-causing diverticulitis.
- Peptic ulcer: Peptic ulcer is represented by the appearance of open ulcers in the wall of the stomach or the upper part of the small intestine, and a peptic ulcer that forms in the stomach is known as a gastric ulcer, and ulcer that forms in the upper part of the intestine is duodenal ulcer, and stomach pain is the most common symptom of peptic ulcer, as for the causes of the peptic ulcer it is often caused by infection with H. pylori bacteria known as stomach germ, or as a result of prolonged use of aspirin medication and antibodies It is worth noting that stress, psychological stress, and eating spicy foods do not lead to stomach ulcers, but may only increase the severity of symptoms.
- Hemorrhoids: Hemorrhoids are the appearance of lumps containing a group of swollen blood vessels in the area, which causes pain and itching in or around the anus, and also causes light bleeding when defecating in some cases, and here it is worth noting the need to see a doctor in all cases where blood with feces is observed.
- Flatulence: Flatulence or bloating occurs as a result of the accumulation of gases in the digestive tract, which leads to a feeling of fullness of the abdomen and the observation of an increase in its size in some cases, as the affected person may feel discomfort or pain.
- Constipation: Constipation can be defined as a decrease in the number of bowel movements than the normal range estimated on average three times a week, but the number of bowel movements and the nature of bowel movements varies from person to person, so it can be said that constipation is a decrease in the rate of defecation than the normal rate of the person and accompanied by difficulty in excreting feces, and the incidence of constipation often occurs as a result of not eating sufficient amounts of fiber or a sudden change in the routine or diet of the person.
- Diarrhea: Diarrhea is known as the protrusion of watery stools three or more times per day, and diarrhea may be severe and last for a short period not exceeding two days and go away without the need for treatment mostly, or may last longer in some cases which may indicate a more serious health problem, as for chronic diarrhea is diarrhea that lasts for an estimated period of four weeks or more, and this type of diarrhea may be continuous or intermittent, and may also be caused by infection with one of the chronic health problems.
- Heartburn: Heartburn or heartburn is a common health problem caused by stomach acid or some of its components bouncing back into the esophagus, leading to burning or pain under the chest or in the area of the head of the stomach.
- Gastroesophageal reflux: Gastroesophageal reflux (GORD) occurs as a result of stomach acid reflux into the esophagus as well, and this condition is often caused by weakness in the sphincter located below the esophagus that separates the stomach from the esophagus, and gastroesophageal reflux is a common health problem that may occur accidentally, or a person may suffer from it for long periods of life, and this health problem may be accompanied by heartburn in the stomach, and a feeling of an annoying taste in the back of the mouth.
- Irritable bowel syndrome: Many people suffer from irritable bowel syndrome or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and this problem often accompanies the person for his life, and its symptoms of diarrhea, constipation, bloating, and stomach cramps appear intermittently, and can last for several days or even weeks and months in some cases, so IBS may have a significant negative impact on the life of the affected person in some cases.
- Inflammatory bowel disease: expresses inflammatory bowel disease IBD is abbreviated from a group of health problems that affect the digestive system and lead to its inflammation, which leads to swelling and redness of the affected area, and the feeling of pain in some cases, and both Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are one most common types of inflammatory bowel disease, and these two diseases are accompanied by similar symptoms including fever, abdominal pain, and diarrhea, and it is worth noting that inflammatory bowel disease may affect women in a slightly different way than men, it may lead to some problems that They affect a woman's ability to conceive, and the severity of the symptoms associated with this disease increases during the menstrual periods.
- Gastroenteritis: Gastroenteritis occurs as a result of a viral, bacterial, or parasitic infection, and leads to suffering from vomiting, diarrhea, and pain in the abdomen in some cases, and diarrhea, in this case, may be caused by inflammation of the lining of the intestine, which affects the nature of its work and leads to its disorder, and this infection can be transmitted as a result of contact with an infected person, or as a result of eating contaminated food or touching contaminated surfaces.
How to keep your digestive system healthy
- A healthy diet is rich in fiber because fiber increases bowel movement which reduces the risk of constipation.
- Reduce high-fat foods, because fats reduce bowel movement which increases the risk of constipation.
- Drink water in ample quantities.
- Exercise regularly.
- Avoid bad habits such as smoking, drinking alcohol, and excessive caffeine drinking.